Introduction:
Oral health is critical to our overall well-being, and maintaining healthy gums and teeth is essential. One common issue many people face is gum recession, which can have various causes. One significant factor that often contributes to gum recession is teeth grinding, also known as bruxism. In this blog post, we will explore the relationship between gum recession and teeth grinding and discuss ways to prevent and treat these issues.
Understanding Gum Recession:
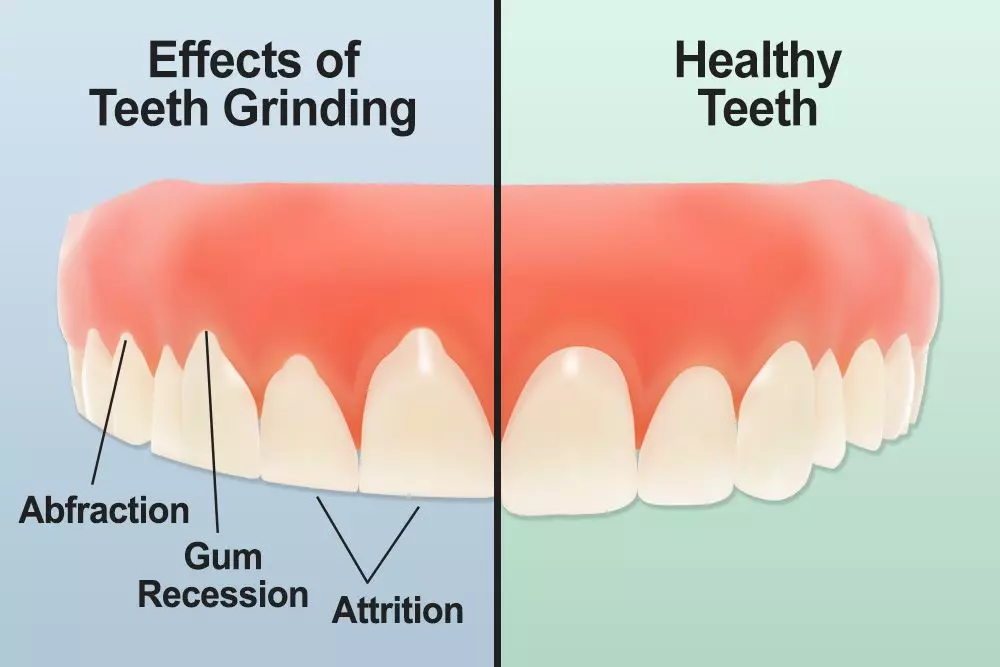
Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth starts to pull back or wear away, exposing more of the tooth’s root. This can lead to several problems, including increased tooth sensitivity, cosmetic concerns, and, in severe cases, tooth loss. A variety of factors, such as genetics, periodontal disease, poor dental hygiene, and trauma can cause gum recession. Teeth grinding is another significant contributor to gum recession.
The Role of Teeth Grinding:
Teeth grinding, or bruxism, involves the clenching or grinding of teeth, often unconsciously, and can occur during sleep or while awake. The intense pressure exerted on the teeth and gums during grinding can lead to several oral health issues, including gum recession. Here’s how it happens:
- Excessive Force: When you grind your teeth, you apply excessive force to your teeth and the surrounding gum tissue. This force can cause the gums to recede over time.
- Abrasion: The friction generated during teeth grinding can wear down the enamel on your teeth and the gum tissue. As the gums become thinner and more fragile, they are more likely to recede.
- Microtrauma: Persistent grinding can result in microtrauma to the teeth and gums. Over time, these repeated minor injuries can contribute to gum recession.
Preventing Gum Recession Due to Teeth Grinding:
Preventing gum recession related to teeth grinding is crucial for maintaining good oral health. Here are some steps you can take:
- Wear a Mouthguard: One of the most effective ways to protect your teeth and gums from the effects of bruxism is to wear a custom-made mouthguard. This device cushions the impact of grinding and prevents further damage.
- Stress Management: Stress is a common trigger for teeth grinding. Engage in stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or therapy to help reduce the likelihood of grinding.
- Dental Checkups: Regular dental checkups can help identify gum recession and teeth grinding early on. Your dentist can recommend appropriate treatments and preventive measures.
- Proper Dental Hygiene: Maintain good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing, to reduce the risk of gum disease, which can exacerbate gum recession.
Treatment Options:
If you’re already experiencing gum recession due to teeth grinding, there are treatment options available. These may include gum grafting to restore lost gum tissue, scaling and root planing to address gum disease, and other surgical procedures depending on the severity of the recession.
Conclusion:
Gum recession is a common oral health issue that can be exacerbated by teeth grinding. Recognizing the link between these two problems is essential for preventing and addressing them effectively. If you suspect you have bruxism or are experiencing gum recession, consult with your dentist for a personalized treatment plan to protect your teeth and gums for years to come. Remember, early intervention and good oral hygiene are key to maintaining a healthy smile.