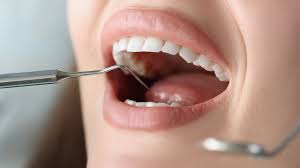
Bleeding gums can be a cause for concern and discomfort, but with proper understanding, treatment, and prevention measures, you can alleviate this issue and maintain good oral health.
What Causes Bleeding Gums?
There are several reasons why gums may bleed:
1. Poor Oral Hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly can lead to plaque buildup, causing gingivitis, an early stage of gum disease characterized by inflamed and bleeding gums.
2. Gingivitis: This condition occurs when plaque accumulates along the gumline, causing inflammation. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease.
3. Vitamin Deficiency: A deficiency in vitamin C or vitamin K can weaken blood vessels, leading to bleeding gums.
4. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy or puberty can make gums more susceptible to bleeding.
5. Medication: Some medications, such as blood thinners or antiplatelet drugs, can increase the likelihood of bleeding gums.
6. Other Health Conditions: Certain systemic diseases like diabetes or leukemia can also contribute to gum bleeding.
Will Bleeding Gums Stop on Their Own?
While occasional bleeding gums may stop on their own, persistent bleeding is a sign of an underlying issue that requires attention. Ignoring bleeding gums can lead to worsening gum disease and potential tooth loss.
Treatment Options for Bleeding Gums:
1. Improved Oral Hygiene: Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily can help remove plaque and prevent gum disease.
2. Regular Dental Cleanings: Professional cleanings by a dentist or dental hygienist can remove tartar buildup that brushing and flossing alone cannot address.
3. Gum Disease Treatment: For more advanced gum disease, treatments like scaling and root planing, antibiotics, or surgical interventions may be necessary.
4. Addressing Underlying Health Issues: If bleeding gums are due to vitamin deficiencies or systemic diseases, addressing these underlying issues can help alleviate the problem.
Preventing Bleeding Gums:
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash regularly are crucial for preventing plaque buildup and gum disease.
2. Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall oral health.
3. Regular Dental Check-ups: Routine dental visits allow for early detection and treatment of any oral health issues before they escalate.
4. Avoid Tobacco Products: Smoking and chewing tobacco can contribute to gum disease and other oral health problems.
5. Manage Stress: Stress can weaken the immune system and make gums more susceptible to infection, so practicing stress-reduction techniques can benefit oral health.
In conclusion, while bleeding gums can be concerning, they are often a sign of a manageable issue like gum disease or vitamin deficiency. By practicing good oral hygiene, addressing underlying health issues, and seeking professional dental care when needed, you can effectively treat and prevent bleeding gums, promoting overall oral health and well-being.